Blog SEO Guide: Rank on Google's First Page in 2026
22nd January 2026
Publishing high-quality technical content does not automatically result in search engine visibility. Many blogs remain undiscovered due to missing foundational SEO components. This guide outlines a structured, repeatable approach to improving search visibility by implementing technical SEO, structured metadata, and automation best practices.
The goal is to ensure that search engines can discover, crawl, understand, and index website content efficiently.
Websites without basic SEO configuration commonly exhibit the following issues:
sitemap.xmlrobots.txtAs a result, search engines may not index the site or may fail to rank it appropriately.
Search Engine Optimization focuses on improving how search engines interpret a website. Core components include:
All components contribute to discoverability and ranking.
Before optimizing SEO, analytics should be enabled to measure performance.
Add the Google tag (gtag.js) to all pages:
<script async src="https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=<GA_ID>"></script>
<script>
window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || [];
function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);}
gtag('js', new Date());
gtag('config', '<GA_ID>');
</script>
This script belongs in the <head> section and enables tracking of organic traffic,
user behaviour, and content engagement.
The robots.txt file guides search engine crawlers.
Example:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Sitemap: https://your-domain.com/sitemap.xml
User-agent: *
Disallow: /assets/vendor/Key points:
A sitemap provides a structured list of URLs for search engines.
Example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<url>
<loc>https://your-domain.com/</loc>
<lastmod>2026-01-13</lastmod>
<changefreq>weekly</changefreq>
<priority>1.0</priority>
</url>
<url>
<loc>https://your-domain.com/blogs/sample-post.html</loc>
<lastmod>2026-01-12</lastmod>
<changefreq>monthly</changefreq>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url>
</urlset>Recommended priorities:
Recommended <head> metadata:
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Technical Blog | Cloud and DevOps Topics</title>
<meta name="description" content="Technical articles covering cloud computing, DevOps practices, infrastructure automation, and modern software engineering.">
<meta name="keywords" content="Cloud, DevOps, Infrastructure, Automation, Software Engineering">
<meta name="author" content="Site Author">
<meta name="robots" content="index, follow">
<link rel="canonical" href="https://your-domain.com/">Best practices:
<meta property="og:type" content="website">
<meta property="og:url" content="https://your-domain.com/">
<meta property="og:title" content="Technical Blog">
<meta property="og:description" content="Insights on cloud, DevOps, and software engineering.">
<meta property="og:image" content="https://your-domain.com/assets/og-image.jpg">
<meta property="og:site_name" content="Technical Blog"><meta name="twitter:card" content="summary_large_image">
<meta name="twitter:title" content="Technical Blog">
<meta name="twitter:description" content="Insights on cloud, DevOps, and software engineering.">
<meta name="twitter:image" content="https://your-domain.com/assets/og-image.jpg">Generic example using Person or Organization schema:
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Technical Blog",
"url": "https://your-domain.com",
"description": "A technical blog focused on cloud computing, DevOps, and automation."
}
</script>Structured data improves content understanding and eligibility for rich results.
<meta name="author" content="Site Author">
<meta name="robots" content="index, follow">
<link rel="canonical" href="https://your-domain.com/blogs/post.html"><meta property="og:type" content="article">
<meta property="og:title" content="Blog Post Title">
<meta property="og:description" content="Summary of the blog post">
<meta property="article:published_time" content="2025-11-05T00:00:00+00:00"><script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "BlogPosting",
"headline": "Blog Post Title",
"description": "Summary of the blog post",
"datePublished": "2025-11-05",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Site Author"
}
}
</script>Process:
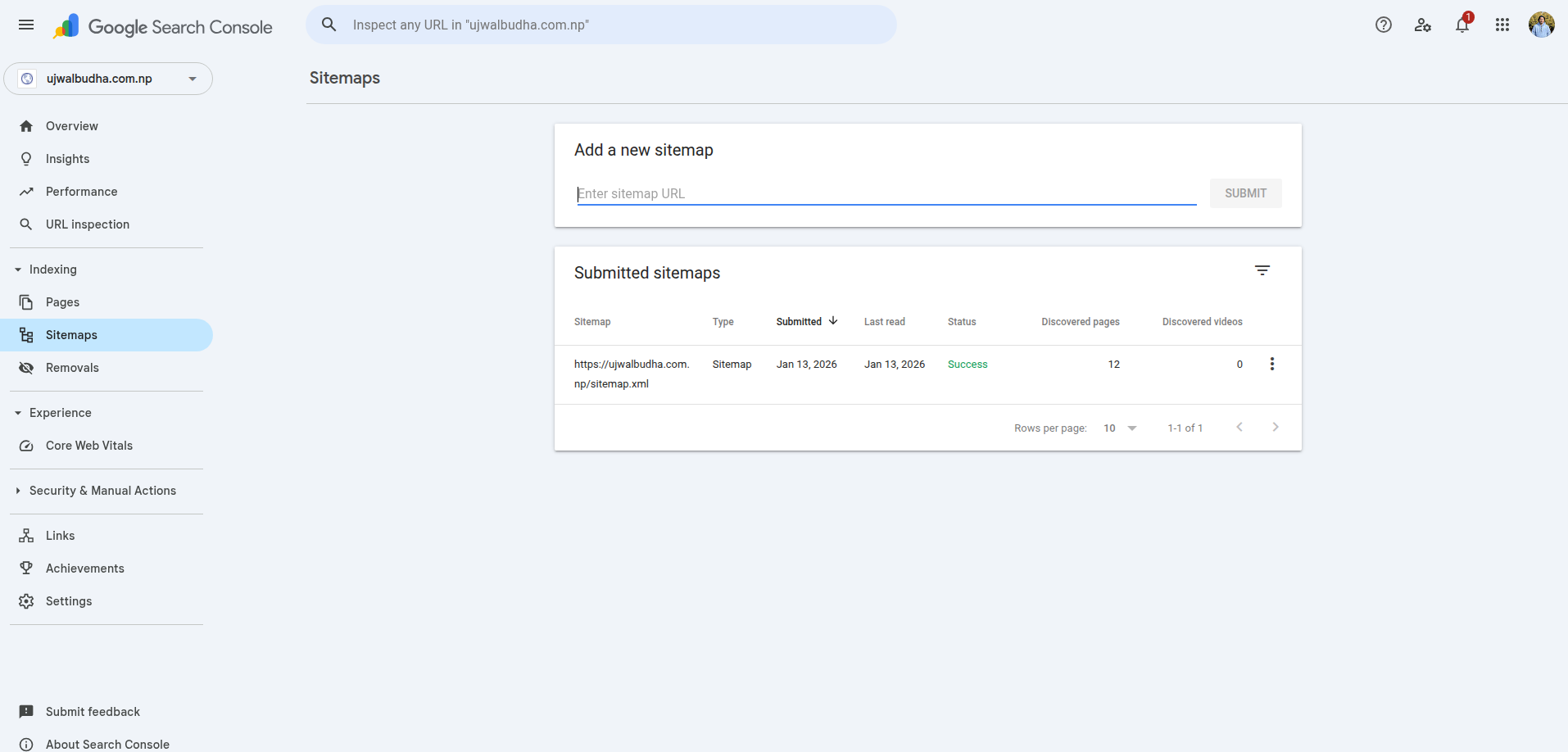 Fig: Google Search Console
Fig: Google Search Console
The URL Inspection tool can be used to request faster indexing of important pages. This is optional once a sitemap is submitted.
Sitemap automation prevents manual errors and ensures consistency.
Typical workflow:
This approach ensures search engines always receive up-to-date URLs. For my use case, I have used a CI/CD pipeline. You can reference it at https://github.com/UjjwalBudha/portfolio.
Key metrics to monitor:
Typical progression:
After implementing the SEO practices outlined above, measurable ranking improvements can be observed for multiple blog posts. This section demonstrates how properly optimized content can achieve first-page visibility for relevant search queries.
The following examples illustrate typical outcomes once pages are indexed and SEO signals mature:
Example 1: A blog post targeting a specific technical problem ranks on Page 1 (position 3) within 2 hours of indexing.
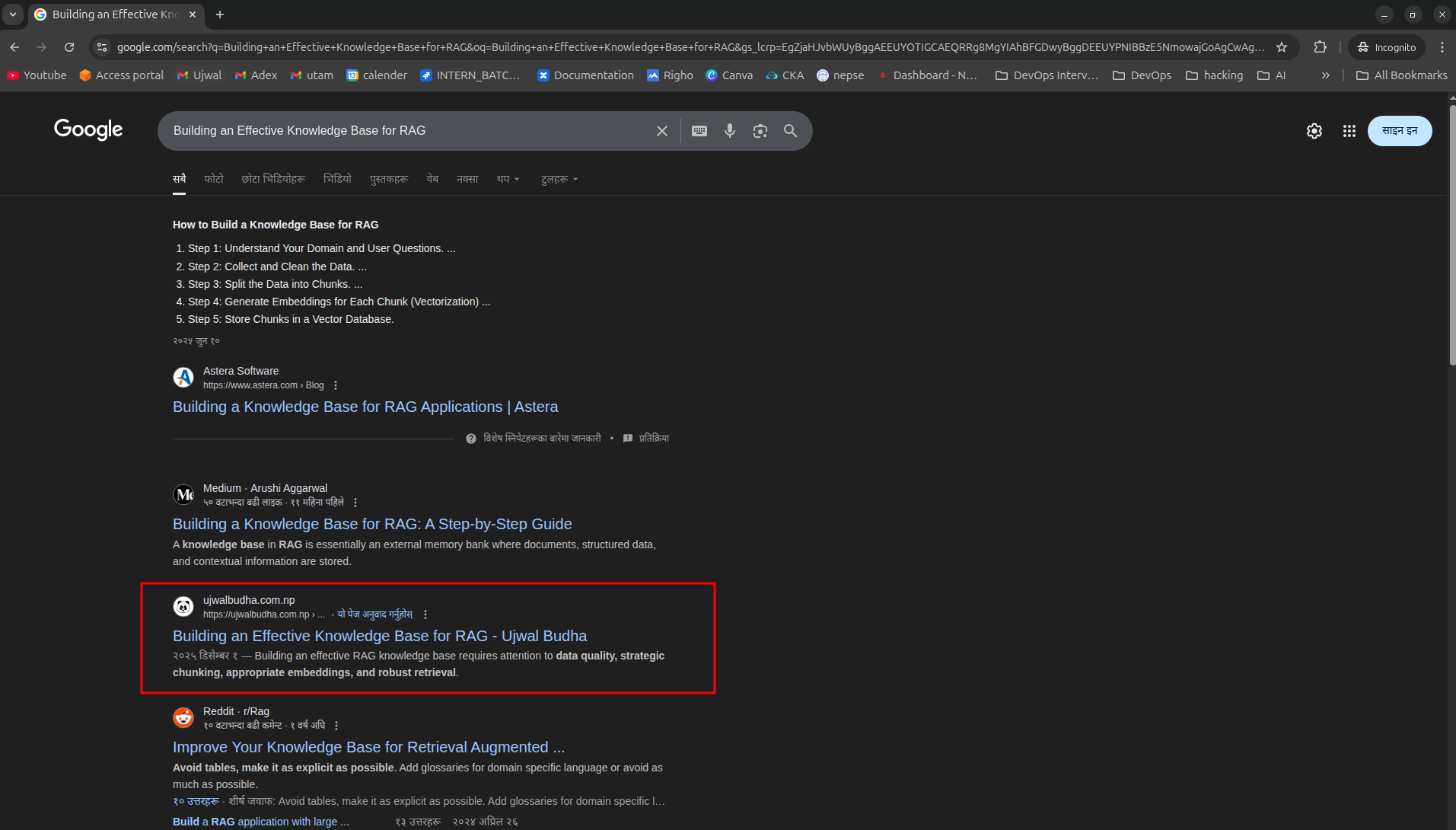 Fig: Example 1 - First-page ranking achievement
Fig: Example 1 - First-page ranking achievement
Example 2: Another blog post targeting a specific technical problem ranks on Page 1 (position 3) within 2 hours of indexing.
 Fig: Example 2 - First-page ranking achievement
Fig: Example 2 - First-page ranking achievement
SEO is a continuous process. By implementing technical foundations, structured metadata, and automation, any technical blog or website can significantly improve search visibility.
Search engines reward clarity, consistency, and structure. Start with the basics, layer in advanced optimizations, monitor results, and iterate over time.